Dear reader, we present to you our beauty columnist Inessa Tsarkova.
Inessa is an active nutritionist, gastroenterologist, therapist, naturopath and aromatherapist, health coach, integrative medicine doctor with a holistic approach. And now he will share with us his knowledge in the field of both physical and mental health, nutrition and much more. Today we will discuss the issue of solar radiation, which is especially acute in May.
The Sun is the source of life on Earth. It was solar energy that plants learned to use in the process of photosynthesis. From it and water with dissolved minerals, all organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, antioxidants) are created. These substances are part of living organisms and provide all processes of their life.
Likewise, the human body cannot do without sun.
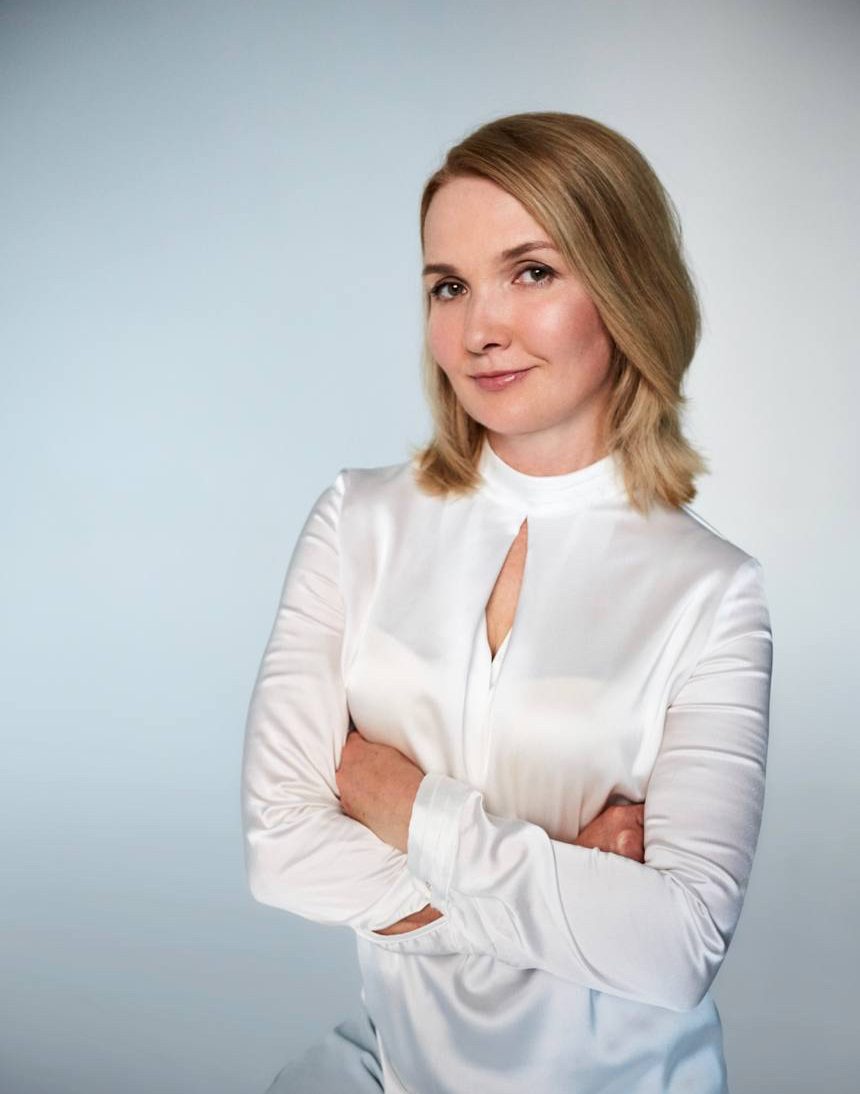

Inessa Tsarkova
For example, sunlight helps convert the amino acid tryptophan into the crucial hormone serotonin. This hormone gives us a feeling of joy and self-confidence, elevates our mood, provides a positive perception of life, is a powerful antidepressant, improves the functioning of the brain, muscles and internal organs, controls sexual function and libido, helps digestion and vascular function. At night, it turns into melatonin, an antioxidant and immunomodulator. This night hormone provides us with adequate sleep, successful recovery processes and the “repair” of all disruptions at the cellular level.
Therefore, sun exposure will be especially beneficial for people with reduced immunity, insomnia, hormonal disorders and seasonal affective disorders.
And this is not all the benefits of sunlight for our prosperous life.
Another extremely important effect of exposure to ultraviolet rays is the production of vitamin D (more precisely vitamin D3) in skin cells.
This vitamin is necessary for the absorption of calcium, prevents the development of osteoporosis, promotes the successful regeneration of bone tissue and prevents growth disorders in children, is necessary for muscle contraction, good functioning of the immune system and protection against many types of diseases. prevention of cancer, autoimmune and cardiovascular diseases, prevention and treatment of type I and II diabetes. It also relieves from depression, is used to treat and prevent respiratory diseases, hormonal disorders, and protects against the development of dementia and multiple sclerosis.
However, certain conditions are needed for vitamin D to be produced in our body: Exposure to UVB spectrum B with a wavelength of 270-315 nm. In this case, the light is absorbed by a special substance in the skin: 7-dehydrocholesterol (the precursor of cholesterol) is converted first into a previtamin, and then into the same vitamin D3. The most important factors affecting previtamin D3 production are the amount (intensity) and quality (corresponding wavelength) of solar UV radiation. These conditions are necessary to reach 7-dehydrocholesterol deep in the basal and spinous layers of the skin.
Fulfillment of these conditions will be affected by: time of year, time of day, geographical latitude, altitude, cloudiness, presence of smog (in cities), skin type and the amount of melanin in it (protects the body from harmful factors). effects of solar radiation and being an antioxidant, stopping oxidative stress), presence and properties of sunscreen, presence of protective cover (clothing or shade).
What are the conditions for exposure to UV radiation for the formation of the required amount of vitamin D?
Fairly moderate exposure to UV radiation, duration – from 5 to 30 minutes and not every day, but 2-3 times a week. You only need to apply it to your bare arms, legs and face. It is important not to use sunscreen. If the skin is darker and UV radiation is weaker, the exposure time should be increased. By the way, unlike the use of nutritional supplements (especially when used in high doses for a long time), it is impossible to overdose on vitamin D during sunbathing.
Solar UV radiation also has a bactericidal effect and helps reduce the activity of pathogenic bacteria and fungi, improving skin immunity (in case of moderate exposure). Sunlight also improves brain functions, dilates blood vessels, improves cell nutrition and oxygen entry into them. And thus it accelerates cell renewal and increases the energy production in them. Sun exposure increases endorphin synthesis, reduces the risk of many diseases and prevents the development of myopia in children.
However, just like a fire with which you can warm yourself and cook food or burn down your house and burn yourself, overly intense and prolonged solar radiation can also harm our body.
The skin and eyes may be primarily affected by its effects. In this case, sunburn (redness, blisters, fever), allergic reactions (urticaria, erythema, itching, blisters), retinal burns, development of solar retinopathy, macular degeneration, cataracts, dry eye syndrome occur. Under the influence of free radicals, the lipid membranes of the cells are damaged, structures in the skin such as sebaleic acid and squalene, which are part of the hydrolipidic mantle of the skin, are destroyed, providing their protective properties and helping to retain moisture in the skin. to preserve its flexibility and youth. Excessive exposure to the sun causes dryness and accelerated aging of the skin, collagen and elastin damage, the appearance of freckles, moles and age spots, and when the immune system is weakened, mutations in cancer-causing cells (melanoma, retinoblastoma).
When exposed to intense solar radiation for a long time, general overheating of the body (heatstroke or sunstroke) may occur. This can cause headaches, dizziness, loss of consciousness, cold sweats, nausea and severe weakness, increased heart rate and increased blood pressure (up to hypertensive crisis), and even cardiovascular accidents (stroke or heart attack).

Long-term exposure to active sun is undesirable, especially for pregnant women. Because excessive solar radiation, among other things, reduces the amount of vitamin B9 (or folic acid) in the blood, which is important for fetal development.
How can we protect the body from the excessive and negative effects of solar radiation?
The most famous and popular protection using SPF creams turned out to be very controversial. Scientists have discovered the harmful effect of such sunscreens on the growth of cancer and premature aging of the skin.
The fact is that solar UV radiation that affects the skin consists of two types: UVA and UVB. They differ from each other in terms of the depth of penetration into the skin. UV-B penetrates superficially, but quickly causes burns on the skin and the appearance of blisters and rashes on it, followed by peeling and peeling. In this case, damaged cells with possible DNA defects are removed from the skin surface and replaced with new, healthier cells. In fact, this process is a kind of indicator of the intensity of exposure to sunlight and the body’s protective response. And it’s exactly this type of sun exposure that the most popular sunscreens with SPF filters are designed to limit.
The situation is completely different with ultraviolet type A, which is not blocked by these protective cosmetics. These rays penetrate deep into the layers of the skin and contribute to the formation of a tan. However, they can also cause serious damage to our cells. They significantly damage them, disrupting immune defenses, changing molecules and causing mutations in DNA. All this can lead to rapid aging of the skin and the development of cancer.
In addition, the explosive cocktail of chemical components in SPF products under the influence of aggressive solar radiation does not care for our skin at all, but on the contrary can act as free radicals and damage cells. And these substances can penetrate the blood, accumulate in the body and harm it from the inside. So, in one study, benzophenone-3 (oxybenzone), a common UV filter found in many sunscreens, was detected in 96% of 2,000 American urine samples.
The best protection against overexposure to the sun is natural methods and a sensitive approach to sun treatments.
Try to follow seven important rules to maintain healthy and young skin.
Sunbathing in the “inactive” sun – Before 10:00–11:00 and after 15:00–16:00 hours.
Gradually increase sun exposure, starting at 15.–20 minutes a day (in this case, the skin will produce more and more protective melanin every day).
Always wear a hat (preferably with a visor).
Try to wear light-coloured clothes when going for a walk.
It is recommended to be under a canopy (in diffused light) or indoors during active sunlight..
Protect your eyes with high-quality sunglasses with broad-spectrum UV filters.
Always have a bottle (or better yet, a thermal mug) with you of warm water (water at 38°C).–40 degrees is absorbed faster and quenches thirst faster).
It may be helpful to add lemon juice or natural therapeutic grade essential oils to your water to add antioxidant properties.
My dear readers, be wise and prudent and exercise moderation in everything. Remember that here too the balance between excessive exposure to solar radiation and its deficiency is very important. Remember that the sun can be both our friend and our enemy.
Source: People Talk
I’m Roger Gritton, and I’ve been writing for the The Fashion Vibes for over 5 years now. My specialty is beauty news; I’m passionate about covering the latest trends, products, and innovations in the industry. In my time there, I’ve become known as an authority on all things beauty-related.
I love discovering new experts to interview, researching up-and-coming ingredients and techniques that are making their way onto our beauty shelves and highlighting people who are making a difference in the world of cosmetics. My work has appeared not only on The Fashion Vibes, but also several other publications including the New York Times Magazine, Allure Magazine and Refinery29.





